Fuel pump device
Used on a variety of types of transport and equipment, it is based on the combustion of the fuel-air mixture and the energy released as a result of this process. But in order for the power plant to function, fuel must be supplied in portions at strictly defined moments. And this task lies with the power supply system included in the design of the motor.
Engine fuel supply systems are made up of a number of components, each with a different task. Some of them filter the fuel, removing contaminants from it, others meter and supply it to the intake manifold or directly to the cylinder. All these elements perform their function with the fuel that still needs to be supplied to them. And this is provided by the fuel pumps used in the designs of the systems.
Complete pump
Like any liquid pump, the task of the assembly used in the design of the motor is to pump fuel into the system. Moreover, almost everywhere it is necessary that it be supplied under a certain pressure.
Fuel pump types
Different types of engines use their own types of fuel pumps. But in general, all of them can be divided into two categories - low and high pressure. The use of one or another node depends on the design features and the principle of operation of the power plant.
So, for gasoline engines, since the flammability of gasoline is much higher than diesel fuel, and at the same time the fuel-air mixture from a third-party source ignites, high pressure in the system is not required. Therefore, low pressure pumps are used in the design.
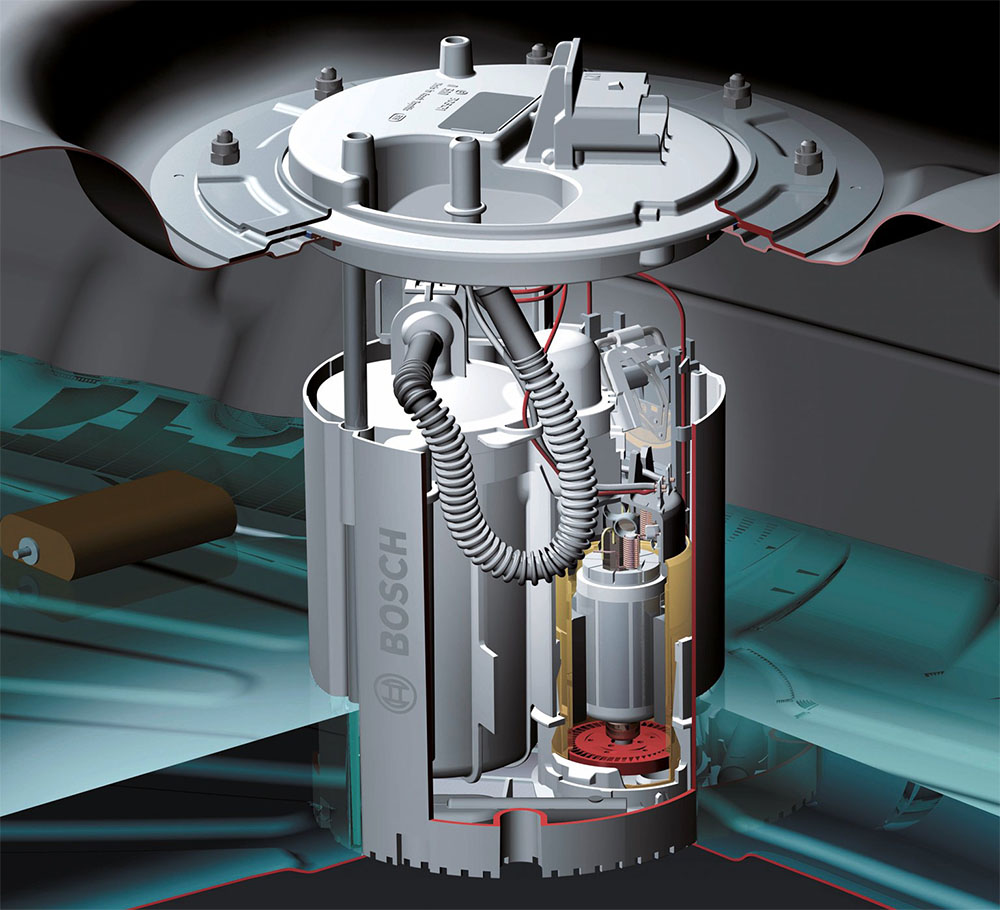
Gasoline engine pump
But it is worth noting that in the latest generation gasoline injection systems, fuel is supplied directly to the cylinder (), so gasoline must already be supplied at high pressure.
As for diesel engines, their mixture ignites under the influence of pressure in the cylinder and temperature. In addition, the fuel itself has direct injection into the combustion chambers, therefore, in order for the nozzle to be able to inject it, significant pressure is needed. And for this, a high-pressure pump (TNVD) is used in the design. But we note that it was not possible to do without the use of a low-pressure pump in the design of the power system, since the high-pressure fuel pump itself cannot pump fuel, because its task is only to compress and supply to the nozzles.
All pumps used in power plants of various types can also be divided into mechanical and electrical. In the first case, the assembly is powered by a power plant (a gear drive is used or from shaft cams). As for the electric ones, they are driven by their electric motor.
More specifically, on gasoline engines, power systems use only low-pressure pumps. And only in the direct injection injector there is a high-pressure fuel pump. At the same time, in carburetor models, this unit had a mechanical drive, but in injection models, electrical elements are used.
Mechanical fuel pump
In diesel engines, two types of pumps are used - low pressure, which pumps fuel, and high pressure, which compresses diesel fuel before it enters the nozzles.
The diesel fuel priming pump is usually mechanically driven, although there are also electric models. As for the high-pressure fuel pump, it is put into operation from the power plant.
The difference in pressure generated between low and high pressure pumps is very striking. So, for the operation of the injection power system, only 2.0-2.5 bar is enough. But this is the working pressure range of the injector itself. The fuel pumping unit, as usual, provides it with a little excess. So, the pressure of the fuel injector pump varies from 3.0 to 7.0 bar (depending on the type and condition of the element). As for carburetor systems, gasoline is supplied there with practically no pressure.
But in diesel engines, very high pressure is needed to supply fuel. If we take the latest generation Common Rail system, then in the “high-pressure fuel pump-injector” circuit, diesel fuel pressure can reach 2200 bar. Therefore, the pump is powered by a power plant, since it requires a lot of energy to operate, and it is not advisable to install a powerful electric motor.
Naturally, the operating parameters and the pressure generated affect the design of these units.
Types of gasoline pumps, their features
We will not disassemble the device of the gasoline pump of the carburetor engine, since such a power system is no longer used, and structurally it is very simple, and there is nothing special about it. But the electric fuel injection pump should be considered in more detail.
It is worth noting that different machines use different types of fuel pumps that differ in design. But in any case, the assembly is divided into two components - mechanical, which provides fuel injection, and electrical, which drives the first part.
Pumps can be used on injection vehicles:
- vacuum;
- roller;
- Gear;
- centrifugal;
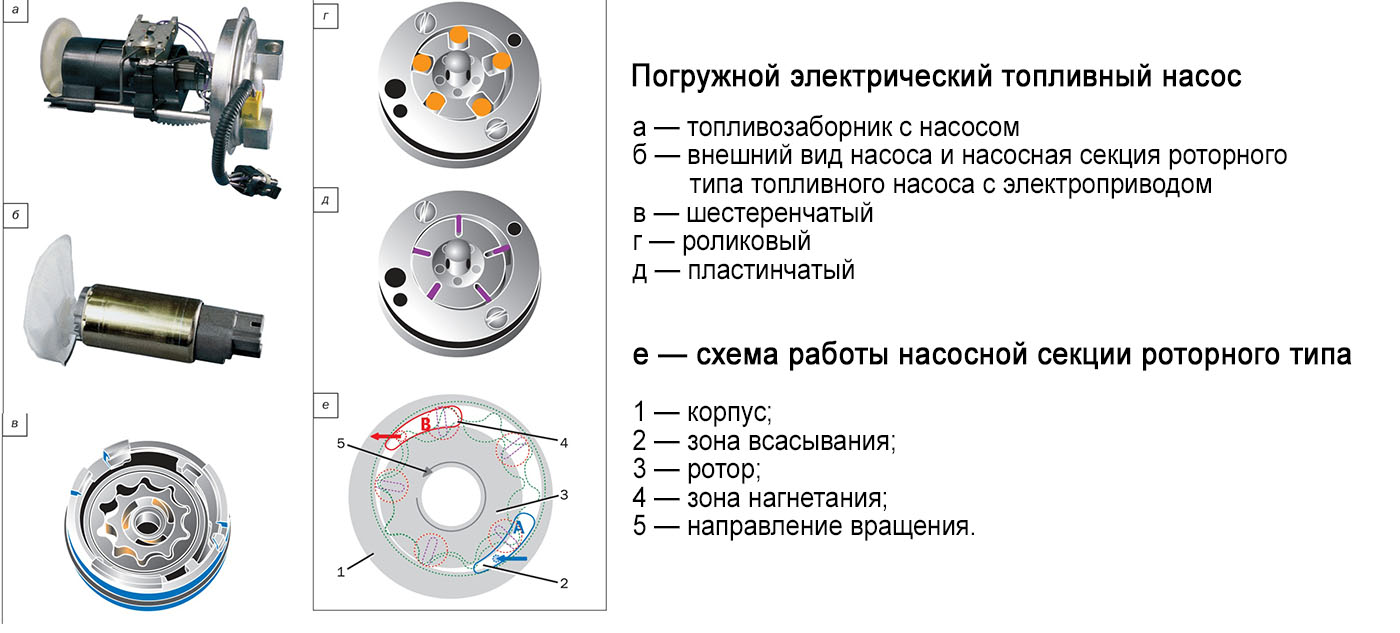
Rotary pumps
And the difference between them basically comes down to the mechanical part. And only the device of the vacuum type fuel pump is completely different.
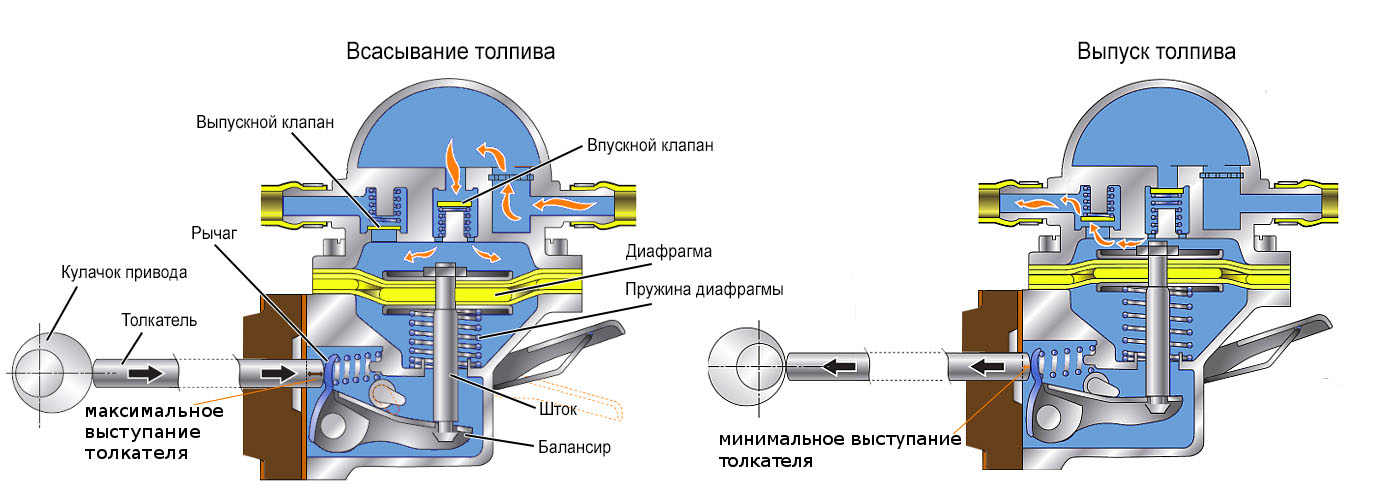
Vacuum
The operation of the vacuum pump is based on a conventional gasoline pump of a carburetor engine. The only difference is in the drive, but the mechanical part itself is almost identical.
There is a membrane dividing the working module into two chambers. In one of these chambers there are two valves - inlet (connected with a channel to the tank) and outlet (leading to the fuel line that supplies fuel further to the system).
This membrane, during translational movement, creates a vacuum in the chamber with valves, which leads to the opening of the inlet element and the pumping of gasoline into it. During the reverse movement, the intake valve closes, but the exhaust valve opens and the fuel is simply pushed into the line. In general, everything is simple.
As for the electrical part, it works on the principle of a solenoid relay. That is, there is a core and a winding. When voltage is applied to the winding, the magnetic field that arises in it draws in the core associated with the membrane (its translational movement occurs). As soon as the voltage disappears, the return spring returns the diaphragm to its original position (return movement). The supply of impulses to the electrical part is controlled by the electronic control unit of the injector.
Roller
As for the other types, their electrical part is, in principle, identical and is a conventional DC motor operating from a 12 V network. But the mechanical parts are different.
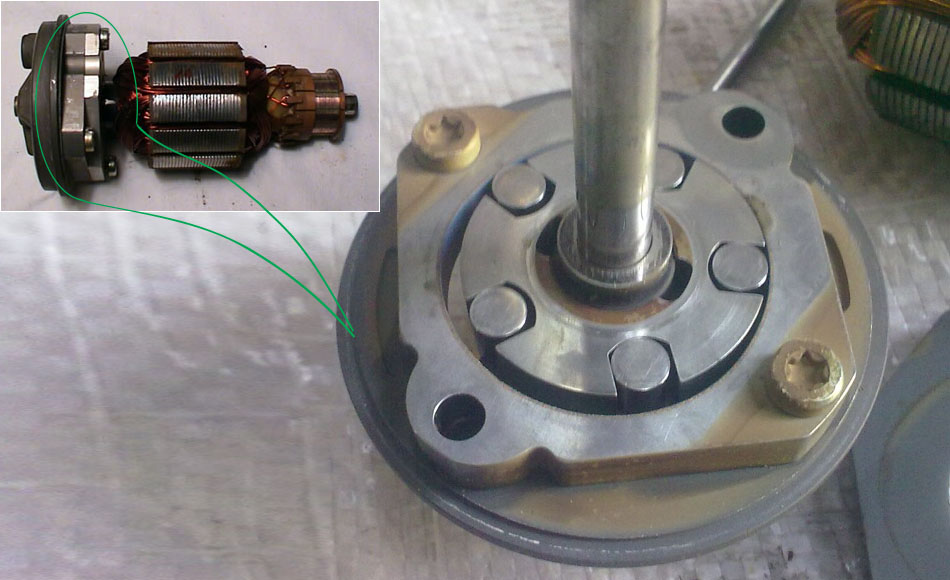
Roller fuel pump
In a roller type pump, the working elements are a rotor with grooves made in which the rollers are installed. This design is placed in a housing with an internal cavity of complex shape, having chambers (inlet and outlet, made in the form of grooves and connected to the supply and exhaust lines). The essence of the work boils down to the fact that the rollers simply distill gasoline from one chamber to the second.
gear
The gear type uses two gears mounted one inside the other. The inner gear is smaller and moves along the path of the eccentric. Due to this, there is a chamber between the gears, in which fuel is captured from the supply channel and pumped into the exhaust channel.
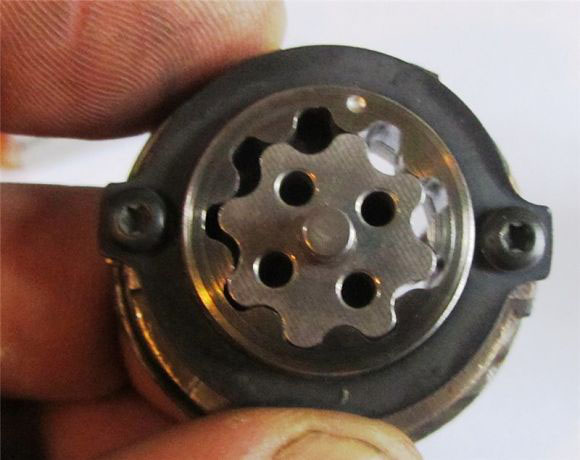

Gear pump
centrifugal type
Roller and gear types of electric fuel pumps are less common than centrifugal, they are also turbine.
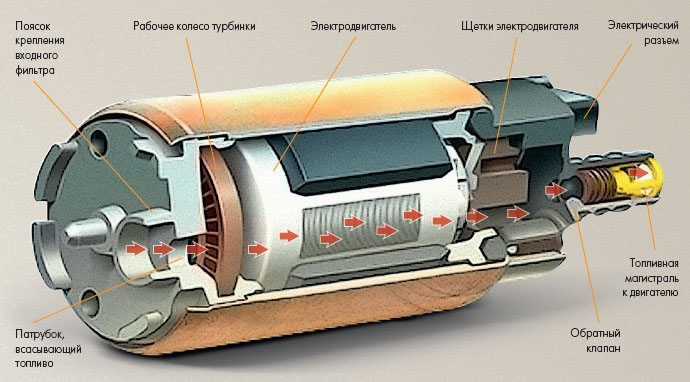
Centrifugal pump
This type of fuel pump device includes an impeller with a large number of blades. When rotating, this turbine creates a swirl of gasoline, which ensures its suction into the pump and further pushing into the line.
We examined the arrangement of fuel pumps in a slightly simplified way. Indeed, in their design there are additional intake and pressure reducing valves, the task of which is to supply fuel in only one direction. That is, the gasoline that has entered the pump can only return to the tank along the return line, passing through all the constituent elements of the power system. Also, the task of one of the valves includes locking and stopping the injection under certain conditions.
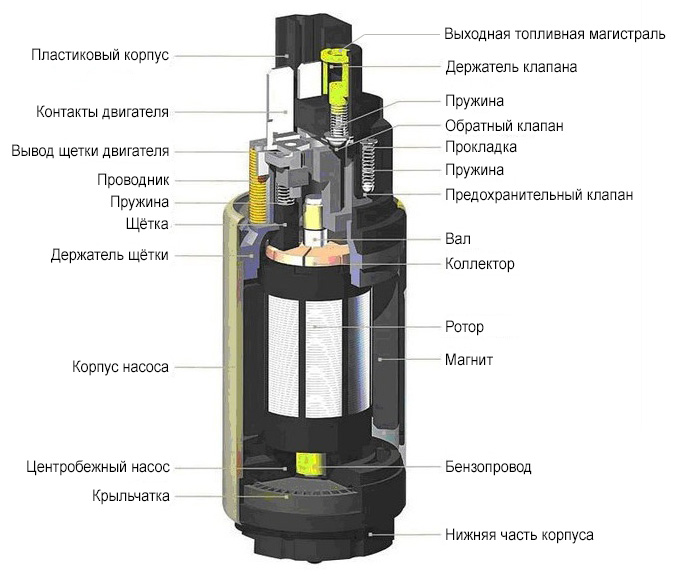

Turbine pump
As for high-pressure pumps used in diesel engines, the principle of operation is radically different there, and you can find out more about such power system components here.




